Search result
 |
 |
|
this article is not available |
||
 |
 |

The battle to secure the internet has been fought for many years. Cybersecurity has remained to be a big challenge for organizations ever since machines in offices go connected to the world wide web. In the early days of the internet, security threats were not as complicated as they are today. Problems facing companies only ranged from a few destructive virus threats to basic scamming attempts. With time though, technology has evolved rapidly and now companies have to deal with complicated cybersecurity threats. Ransomware, data theft, and network disruptions are just some of the threats that face organizations.
The evolution of cybersecurity threats has also prompted an evolution in defense mechanisms. Today, it is not uncommon to see companies that have a fully-fledged cybersecurity department. It is no longer possible to gamble with the security needs of any enterprise. Cybersecurity has thus moved on from being a small aspect of the organization to a core part of every company. There are many great things that have been achieved over the years in the cybersecurity realm, but the many challenges that persist as a result of a rapidly evolving tech realm are just too real to ignore. Jamie Cambell from GoBestVPN recently noted that while it is not possible to completely eliminate threats, it is possible to have better solutions in the market. Recent years have seen companies lose millions of dollars because of security vulnerabilities. Such big losses have prompted companies to think differently. New approaches are being explored in the area of tackling cyber threats.
Security is Now a Core Part of Every Organization

As mentioned earlier, organizations are now taking the cybersecurity issues much more seriously. The security of company data is no longer an issue of the IT departments alone. Instead, it is an organization-wide affair which cuts across all levels of the institution. According to recent reports by Varonis, 41% of companies have been found to leave their data exposed to everyone. Such statistics indicate that the problem is not simply about attacks becoming more complicated. Instead, it is the approach that is taken by organizations that are contributing to vulnerability. Organizations are thus making it a duty to educate every member of the team on the cybersecurity challenges of the modern day.
Indeed, adaptive enterprises have been restructuring their security needs to meet modern-day goals. Security has thus stretched from the small IT department to become a ubiquitous part of daily operations in organizations.
Security is Forcing Technology to Evolve
There are no benefits that come with cyber-attacks. But if there were to be a single positive impact from cyber threats, it has to be innovation. Security in the cyber realms has forced entities to think outside the box. Threats have encouraged innovators to come up with new solutions for a wide range of issues. Indeed, the creativity that has been sparked as a result of security challenges has led innovation not just in the security realm but in the tech industry as a whole. Technologies of the future are now hitting the markets with security implements being incorporated.
Security is Getting Agile

In recent years, testing and analysis approaches have changed in the digital realms. The increasing security threats have forced the industry to adopt agile measures. Cybersecurity solutions are thus now becoming much faster, smarter and robust. The dynamism that has been experienced in the industry has allowed for the faster collection of data, quick analysis and almost immediate response to threats. As security stakeholders develop the next generation of solutions, the lessons that have been learned will definitely prove to be crucial. The collection and use of data are changing and this makes security solutions much more dependable.
What Does the Future Look Like for Security?
The industry will definitely continue to evolve. Cybersecurity issues are unlikely to go away and this will force enterprises and organizations to continue creating solutions. While it is not possible to predict exactly what will happen, it is sensible to assume that new technologies will provide more robust protection. As faster technologies become mainstream, it will be difficult for attackers to beat the pace of strong systems. Businesses will nevertheless need to take security issues much more seriously as the technology moves to the next stages.

The internet connects more people today than any other time since it was introduced. As of stats from 2019, almost 4.13 billion of the world's 7.7 billion people have access to the internet. This extensive reach brings accessibility, feasibility and convenience to a lot of people but as times progress, the number of threats on the World Wide Web are growing substantially. In 2019 alone, more than $5 trillion were lost to cybercrime activities across the globe.
This number, however, doesn't include the amount of threats that user data faces because it has risen to become one of the most sought-after commodities with organizations and brands sometimes going overboard in their quest to gather relevant information about consumers or people in general. These are just a couple of reasons which make it imperative for users to hide their identity while online. Here we discuss online privacy issues and how a VPN for Windows can help resolve them.
Privacy threats on the internet
There is a diverse range of threats on the internet these days. Different organizations, businesses and people have various agendas that they want to fulfill. They employ multiple ways to achieve this and at the end of the day, the victims are normal internet users. Over the years, cybercriminals have become exceptionally active and the way they target individuals and businesses is constantly evolving. Some of the challenges that users face online include:
Phishing
The activity gets its name from regular fishing because cybercriminals use bait to lure unsuspecting victims into their trap. Phishing can happen over calls, text messages, emails, social media platforms or just simply while you are browsing the internet too. Random links, email attachments or calls asking for sensitive information with the person on the other end posing like the representative of a bank can trick people into giving out some of their private information.
Social engineering
Social media has made it easier to connect with almost anyone around the world but it has also put a lot of our personal information online. Hackers can use this information to study a potential victim. Then, they act like a boss, colleague, friend, family member or some other social contact with the intention of making the victim give out personal information. This technique is growing in usage quite fast and many people are falling for it.
Malware
This includes a host of viruses, bug and other elements that may infect a user's device. There is a host of malware that has been detected and new ones are being discovered regularly. Trojans, spyware, adware, ransomware, bots, bugs are all different forms of malware. Each one has their own unique characteristics and functions. They can live within a system for extended durations without the user noticing their existence.
These threats don't include internet service providers or brands monitoring data traffic through the use of IP addresses. Together, these activities necessitate the use of a VPN for Windows.
How a VPN for Windows keeps you anonymous
Many of you may be wondering why a VPN? A VPN is one of the most effective tools to hide IP address of users by rerouting normal internet data traffic. An IP address is like the virtual location of a system when it is connected to the internet and by default, it is public. Anyone with the right tools can easily find out what the IP address of a particular device is. This can open a window of opportunities that can cause an array of damages to the other person.
A VPN offers features that can help eliminate many of these vulnerabilities that exist in the network. A few of these include:
Secure servers
In a normal internet connection, data packets are first sent to the internet service provider and then to the website which a user is trying to access. The ISPs usually monitor and keep logs of all the traffic that goes through them. A VPN helps eliminate this by sending all the data to their own secure servers first and then towards the website. This plugs a critical loophole in the system which exposes user data while they are online.
Encryption
Another problem is the protection of data while it is being sent to various website servers. Hackers these days have the ability to intercept the flow of information and siphon it according to their own convenience. VPNs offer state-of-the-art encryption protocols to prevent data from being stolen while in transit. Leading VPN services have AES 256-bit encryption protocols which are the most secure and highest level commercially available so far.
Advanced threat detection and prevention
Besides protecting the outgoing data against potential threats, the top VPN services also offer detection and prevention for malware that may be incoming. There are various features that help warn users about spam emails or dangerous viruses that are directed towards and trying to make their way into the system of a user.
Using features like secure servers and encryption protocols, VPNs make sure that users remain anonymous while they are online because no one knows their location or identity whatsoever.
Other benefits of a VPN
The anonymity that a VPN offers can come in handy for more than just protecting against data breaches. Many websites on the internet resort to content restrictions because of various reasons. This can become a huge nuisance at times because it hinders easy and free access to the internet for many normal users.
Streaming
Netflix, Amazon Prime, Disney+ and other streaming platforms are gaining immense popularity these days. Unfortunately, the content they offer varies. For instance, a show that may be available in the US library can be taken off the UK list etc. This can mean that a US user misses out on their favorite shows in case they are travelling and people living in other countries can't have that particular show either. With a VPN, this issue can be eliminated easily.
Bypassing geographic restrictions
The secure servers of a VPN are spread evenly across the world meaning that users can connect to and enjoy content without any restrictions. This internet freedom allows not just open streaming but also accessing general information online because many business websites also limit access to users in a particular region.
Author Bio:
Scott is a cyber-security professional. He's been writing in the internet privacy niche for a while now and has churned variety of informational pieces to educate his audience. Connect with him on Twitter.

Reports suggests that Microsoft is working on a New Internet Browser for Windows 10, Moving from the good-old bad-old Internet Explorer to the new Microsoft Spartan Browser. The New "Spartan" browser is still in-development. Today though there are a couple of new leaked images doing the rounds, and these two show us a very different design for Spartan.

The actual leaked images are the first two below. Underneath you can see a mockup based on them, which is supposedly a near 1:1 replica of the browser's UI.
Thankfully this time around Spartan looks a lot more modern, yet it still manages to be quite minimalistic. The browser clearly looks more like Chrome and Firefox than IE, and not many will say that's a bad thing. Next to the star for bookmarking purposes lies a "reading mode" button which strips out the text and makes whichever page you're on more readable (this is similar to Safari's Reader Mode).
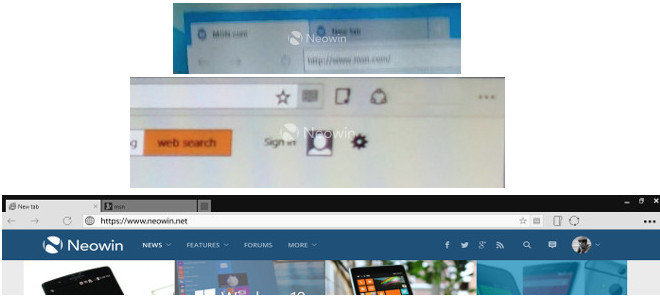
The share icon lets you easily send a link to the current website through social networks or by email, and the three dots on the right are there to open up the settings, as you may have guessed. Spartan's window is borderless, allowing content to stretch from edge to edge. All of the UI elements are at the top.

Having an Internet access while flying is important to stay online while flying, either for work or just entertainment. Many major airlines now offer internet access to their passengers through an on-board Wi-Fi connection. Data is delivered via satellites or from ground-based cellular antennas beaming 3G/4G airwaves at the sky. However, its very expensive, starting from $30 per flight.
To make things easy, Here is a list of Airlines with free Wi-Fi internet access on their flights:
• Norwegian Airlines: has high-speed broadband on flights within Europe. The service is available on the company's Boeing 737-800 aircrafts.
• JetBlue: has all of its Airbus 321s and most of its A320 planes equipped with Wi-Fi gear. There's a catch, however. The free access option imposes restrictions on your connection. To go online at full speed, you'll have to buy a pass.
• Hongkong Airlines: has free Wi-Fi on its Airbus A330-200 aircraft operating from London to Hong Kong. The connection speed, however, is limited for those using a free pass.
• Air China: free Wi-Fi service comes with a catch. Passengers cannot connect to it from their smartphones as these are not allowed to be on during flights. Tablets and laptops, on the other hand, are A-OK.
• Nok Air: provides free Wi-Fi internet access on domestic flights throughout Thailand. The service is only available on two aircrafts, however.

As an Australian who sometimes visits Australia but doesn't live there anymore, let me tell you that when I head back home and fire up the internet I am often sorely disappointed, however not nearly surprised at all.
After a good nine months in Cambodia where the speed of my 4G mobile was faster than my ADSL speed at my parents' house in inner city Perth, I just had to laugh. I have to visit particular sites that don't chew speed to even play new slots games smoothly. From a very poor third world country to coming across to one of the most advanced English speaking first world countries (hey, a lot of Europe, particularly Scandinavia, is streaks ahead of us in most areas) you'd expect the internet speeds to be at least up to the same quality - if not faster.
Yeah, this isn't the case
I know that this is an article about the difference between the bandwidth in the USA and the bandwidth in Australia, but I feel like this is a particularly relevant point to bring up. The internet speeds and bandwidth in Australia suck.
Australia is detached (physically) from the rest of the world
This isn't news. Plus, it isn't even really that surprising. Australia is the most isolated continent on Earth (except Antarctica, which I'm sure expect slow internet due to, oh, the almost non-existent population levels). Australia is very far from the rest of the world. That's what's kept the country from getting invaded by others and starting a war. Who on Earth can be bothered going all that way to attack? Ships would take forever, and planes are too expensive. With drones becoming more prevalent this could be an issue in the future but until then... I'm losing my point here, aren't I?
To get internet to Australia there needs to be undersea cables laid for thousands and thousands of kilometres. What type of cables? How many? What's the bandwidth there? So, that means that there's a finite amount that Australia can receive to begin with without laying more (hugely expensive) cables.
Once it gets to Australia, it's another story. Let's check out the average speeds of the USA compared to Australia at the Speedtest Global Index, shall we?
Australia is currently sitting at number 56 on the list of the top 100 countries, with an average speed of 26.45Mbps. Oh, look, we're one number ahead of Kazakhstan. The US is sitting pretty at number 9 with a speed of 83.20Mbps. Unsurprisingly, Singapore is number 1 (at 166.44Mbps) and Hong Kong at number 3 (136.15Mbps), two of the most technologically advanced cities in the world (Asia), and Iceland at number 2 and 161.98Mbps, which is arguably the most technologically advanced city in Europe. Who's in front of Australia on the list? Wow! Heaps of countries you wouldn't think. Puerto Rice, Uruguay, Chile, Thailand, oh hey - there's even New Zealand at number 21 with 66.89Mbps!
New Zealand??!!
New Zealand is the island country right next door to Australia on the right hand side. Many people are not aware that New Zealand is even a place (or think it's part of Australia) unless they've met a Kiwi or have seen an advertising campaign luring them there - it's where Lord of the Rings is filmed. There is only around 1700km of ocean between New Zealand and Australia.
Why is Australia's internet so slow compared to the US if it's not just geography?
So, really, maybe the title of this article should be why is Australia's bandwidth so woeful compared to the US, or even their closest neighbour?
The answer to this is a bit of a complex riddle that originates with the history of telephony networks in both countries.
In the US, this tracks back to the beginning of telephony. In 1885 AT&T was formed. AT&T held a private monopoly in the US until 1984, when a court ordered the company to split into regional companies. AT&T was, and is, a private company. Telephony networks in the US were never government owned, always private companies.
A brief history of Australian networks
In Australia, the Telstra network was the only telephony network, a government owned and run network, until privatisation in 1997. This is important to note, because by this time internet was prevalent in all parts of Australia, running exclusively on the only network in Australia - Telstra. The privatisation also included allowing other private companies to enter the market.
Of course, the people at Telstra were clever enough to realise that the country is huge with not much "stuff" (aka infrastructure or population) in the middle - unlike the US. "Australia" really describes the coast of Australia - because there is not much else in the rest of it.
While Telstra's infrastructure was and is aging, they owned it all and it was/is the best available. Other providers couldn't compete due to the huge costs of infrastructure implementation.
Eventually, the Australian government saw the stranglehold that Telstra (still) had on the market and recognized their constituent's cries for faster internet. Thus, the NBN was proposed. The NBN or National Broadband Network, was an initiative dreamt up by the then government in 2007 to get Australian internet speeds in line with the rest of the world.
While the NBN was brilliant in theory, it's execution over the past 10 years (continuing) has been woeful. An initial estimated $15 billion cost has now blown out to $56 billion. An original fibre to the node idea changed to fibre to the premises and then again back to fibre to the premises.
Trying to find companies to implement the solution were failures. Trying to find the right technologies were failures. The interactions with Telstra inevitably favoured Telstra as they were the experts in the field. Changes in governments over the years meant changing strategies on the project. The NBN in Australia is currently a national joke.
The state of the NBN today
The NBN's statistics are confusing, some say to hide the fact that they're not living up to expectations. Many households that have connected to the NBN complain that they are receiving slower speeds as compared to their ADSL connection, too.
And it's true - in many cases connecting to the NBN is slower than using the old school ADSL. This is to do with the packages, pricing, offerings, and partnerships. Yes, in a lot of households' instances, it is better to go with the technology that has been in place for years upon years, rather than "upgrading" to the NBN.
If you do a Reddit search for NBN + joke you'll be pleasantly surprised by the amount of results that you uncover. Or, if you're an Australian, mildly irritated, but not surprised. The network that was supposed to bring Australian internet speeds in line with the rest of the world has failed miserably, mainly due to changes in government, which dictates policy, combined with lack of expertise in infrastructure by the people hired to do the job - not surprising when government tenders often go for lowest cost offers to save the budget.
While the NBN is still rolling out it is already obsolete. As a first world nation, Australia is relatively slow on the uptake, particularly as it applies to government understanding of technology, requirements, and the effects of privatisation. In fact, plenty of the NBN is still that good old copper wire the telephony networks ran on back when the government owned Telstra.
Australia would do well to invest in learning about technology before they try to implement it. In comparison to Singapore, who invest heavily in tech and learning the differences are stark.
In comparison to the US, the US is light years ahead. While this is a combination of the differences in geography, policy, and privatisation, the evidence is clear. Australia has a long way to go when it comes to learning how to increase their internet speeds and it looks like this is now squarely in the hands of private companies should they wish to take on the challenge.
And I have no doubt that if one of the private companies had taken on a premise such as the NBN they would have been able to implement the system - actually, a better system - at far less of the cost of the government estimates. It remains to been seen what happens in Australia when it comes to broadband but I can only imagine they'll be trailing behind the rest of the world for some years to come.
So, forget it. I'm taking off from mum's house and heading back to Cambodia where I can stream in peace.

Courtesy of GSM Arena, we are now able to take a look at the Sony Xperia F8331 prior to its launch. In case you are not aware, the F8331 is the upcoming flagship smartphone from Sony and it is supposed to be released in 2016. From what we can see, the device looks quite different in comparison to its predecessors and will probably sport a larger display as well. At the back, the position of the camera and the dual-tone flash have been tweaked slightly to give it a new look. A separate panel at the back and near the bottom can also be seen, which looks similar to an antenna window.

There's also the USB Type-C port, the 3.5mm audio jack, a NFC antenna and the much loved front facing stereo speakers. We found the device to be gorgeous and the specs look promising so far. There might be a few complains about Sony going with a Full HD display for the F8331 instead of a QHD or even 4K display, but considering how much of a battery hog those can be, we are not complaining. You can still shoot 4K videos with both the front and the rear cameras though.

Author: Saikat Kar (tech-enthusiast)
© 2023 YouMobile Inc. All rights reserved





